Cognitive Model: Creating Artificial Intelligence
Prominent organizations worldwide are currently banking largely on the cognitive model; the key to creating artificial intelligence. Artificial intelligence is widely accepted to be the next level of automation that will deliver unprecedented levels of customer value. Unsurprisingly, AI is a core element of innovation strategies of businesses that plan on exploiting this technological disruption.
The concept revolves around allowing machines to learn, reason, think and imagine the way human beings can. Computers can therefore mimic how human beings process information and essentially mimic humanity.
The impacts of this model can be far-reaching and deep. For starters, machines can actually work intelligently on our behalf instead of always under our command. They can analyze situations and make decisions the way we do, thereby easing our workload.
While human beings can process and remember a limited amount of information, computer systems can work with astronomically greater volumes. Such systems can also store and retrieve information in a far more organized manner. If these systems could learn to judge the way we can, they can do most of what we can do, and possibly better than we can.
How Does It Work?
Traditional computing relies entirely on logic. The information fed into the system is judged in the most rational of ways, to come to an extremely logical conclusion. However, human beings don’t always strictly adhere to these logical methods. A host of other variables affect our cognition, such as emotion, fatigue, stress and prejudice among many others.
Cognitive computing takes all these other factors into account to make a more “human” system. Such systems use self-learning algorithms that utilize data mining, pattern recognition and natural language processing to learn about the human brain and behavior. These particularly sophisticated algorithms use deep learning to learn from various levels of structured and unstructured data, picking up on subtle differences in levels of abstraction and concepts. Neural networks work alongside these algorithms, which are essentially complex connections between “units” that process information, much like the connected neurons in our brain.
Such systems continuously acquire knowledge from information being fed into them by mining it for patterns. With experience, the systems themselves refine how they look for patterns and how they process the data thereby constantly developing themselves. Some programs even track the discrepancy between the actual state or behavior of an individual, and what was expected, further enhancing the model. The cognitive model therefore allows computers to predict more accurately how a human would behave and model solutions accordingly.
 This ability to learn from experience is known as machine learning. It involves constructing complex algorithms that can learn from data and make predictions, instead of sticking to static instructions in traditional computer programming. The more these programs are exposed to real-life situations, the more they learn, and the more accurate they become.
This ability to learn from experience is known as machine learning. It involves constructing complex algorithms that can learn from data and make predictions, instead of sticking to static instructions in traditional computer programming. The more these programs are exposed to real-life situations, the more they learn, and the more accurate they become.
Where is the Value Addition?
AI has added value on multiple fronts: transportation, healthcare, manufacturing and management, among others. It has streamlined existing businesses and even developed brand-new businesses, with unprecedented products and services. Here are a few instances of AI adding value to lifestyles everywhere.
Driverless Cars
 Driverless cars being developed by the likes of Google and Mercedes use the fundamentals of the cognitive model. These cars use arrays of sensors to detect their surroundings and move accordingly. The computers aboard these cars continue to learn with every new drive. They can differentiate between objects on the road, whether it is another vehicle, a person or a random animal. They can even recognize traffic signs and stop or adjust the speed according to the speed limit. They can maneuver around obstacles and take precautionary measures in case a collision is imminent.
Driverless cars being developed by the likes of Google and Mercedes use the fundamentals of the cognitive model. These cars use arrays of sensors to detect their surroundings and move accordingly. The computers aboard these cars continue to learn with every new drive. They can differentiate between objects on the road, whether it is another vehicle, a person or a random animal. They can even recognize traffic signs and stop or adjust the speed according to the speed limit. They can maneuver around obstacles and take precautionary measures in case a collision is imminent.
The greatest aspect of this new breed of vehicles is that they learn to be better. They get better at doing every single feature mentioned above, with experience. Human beings get better at driving over the years as they drive more. These cars act just like human beings when it comes to the learning curve. Even if it does make a mistake, it learns from it and almost never makes the same mistake again.
AI in Healthcare
 The health sector is expanding the capability of doctors with the help of intelligent computers that can process massive volumes of data and help in medical diagnosis and treatment. Medical imagery such as X-rays, Gamma scans, and CAT scans can be interpreted with greater ease with the help of intelligent computers. The idea is to augment the capabilities of doctors with the capabilities of these intelligent machines which can spot the tiniest of details in these images. Other applications include using AI to make decisions about diagnosis and treatment plans. IBM’s Watson for instance helps in making decisions about patients in clinical trials and their treatment options. Drug creation and experimental treatment plans could also benefit from cognitive machines.
The health sector is expanding the capability of doctors with the help of intelligent computers that can process massive volumes of data and help in medical diagnosis and treatment. Medical imagery such as X-rays, Gamma scans, and CAT scans can be interpreted with greater ease with the help of intelligent computers. The idea is to augment the capabilities of doctors with the capabilities of these intelligent machines which can spot the tiniest of details in these images. Other applications include using AI to make decisions about diagnosis and treatment plans. IBM’s Watson for instance helps in making decisions about patients in clinical trials and their treatment options. Drug creation and experimental treatment plans could also benefit from cognitive machines.
Intelligent Robots
 Intelligent robots could become a regular sight that could help us in a variety of ways, be it in manufacturing, in healthcare or even in hospitality industries. The automobile industry is highly dependent on robots but the scope of its usage is limited because they are limited by their programming. The robots can hardly deal with situations outside the norm without human intervention. With intelligent robots, many manufacturing industries including the automobile industry can rely on robots efficiently manufacturing products. High-risk tasks can finally be completed without any human intervention at all, making things much safer for workers.
Intelligent robots could become a regular sight that could help us in a variety of ways, be it in manufacturing, in healthcare or even in hospitality industries. The automobile industry is highly dependent on robots but the scope of its usage is limited because they are limited by their programming. The robots can hardly deal with situations outside the norm without human intervention. With intelligent robots, many manufacturing industries including the automobile industry can rely on robots efficiently manufacturing products. High-risk tasks can finally be completed without any human intervention at all, making things much safer for workers.
Intelligent robots are also coming up in other arenas like the hospitality and janitorial industry. From being a bartender and making designer drinks to manning the front desk of a hotel to cleaning floors & keeping restrooms fresh, robots are making waves.
AI-Powered Chatbots
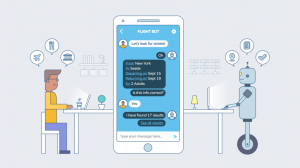 Chatbots are essentially virtual personalities that respond like human beings. Customers can be dealt with using bots, which will talk just like a human customer care rep, but provide more consistent service, at any time of the day. These virtual personalities can even become a friend for the lonely or help people resolve issues.
Chatbots are essentially virtual personalities that respond like human beings. Customers can be dealt with using bots, which will talk just like a human customer care rep, but provide more consistent service, at any time of the day. These virtual personalities can even become a friend for the lonely or help people resolve issues.
Bots are already quite prevalent now. Many organizations have opted for bots to provide 24×7 customer support. While these may be expensive to create, they are much cheaper than keeping a human customer support employee 24/7 in the long run.
Smart Personal Assistants
 Smart personal assistants like Siri, Google Assistant and Cortana have been around for a while. By recognizing commands spoken in natural language, they’ve made our lives way easier. Making helpful suggestions about the weather, traffic information and other factors that affect our daily lives is a testament to how these programs can learn from experience.
Smart personal assistants like Siri, Google Assistant and Cortana have been around for a while. By recognizing commands spoken in natural language, they’ve made our lives way easier. Making helpful suggestions about the weather, traffic information and other factors that affect our daily lives is a testament to how these programs can learn from experience.
The Challenge
The primary challenge in effectively harnessing the cognitive model lies in the large volumes of data needed for such artificial intelligence to be created. Machine learning requires massive volumes of data which algorithms will process and learn. For such programs to make accurate predictions, they have to be exposed to vast data sets that accurately represent various scenarios and outcomes, for them to have an accurate idea of how to deal with such scenarios in the future. The more diverse, accurate and voluminous the data sets, the more “learned” the machine will be.
However, such data sets are quite inaccessible in reality. Data sets that could have such qualities are usually generated by individual users which are strictly protected by privacy laws and are thus inaccessible for the purpose of creating artificial intelligence. Only a handful of companies such as Google and IBM have thus been leading in this sector.
Despite the challenges, machine learning is moving forward at a remarkable pace. More and more companies, both existing titans of the tech world and new startups, are joining the wave and coming up with creative ways to source large data sets.
For a long time now, computers have excelled in the memory aspect of things, but have always lagged behind when it came to learning. Machines could never truly be intelligent. But with the cognitive model at play, machine learning can finally allow computers to be intelligent.